Table of Links
2 Dark matter through ALP portal and 2.1 Introduction
2.3 Existing constraints on ALP parameter space
3 A two component dark matter model in a generic 𝑈(1)𝑋 extension of SM and 3.1 Introduction
3.3 Theoretical and experimental constraints
3.4 Phenomenology of dark matter
3.5 Relic density dependence on 𝑈(1)𝑋 charge 𝑥𝐻
4 A pseudo-scalar dark matter case in 𝑈(1)𝑋 extension of SM and 4.1 Introduction
4.3 Theoretical and experimental constraints
Appendices
D Feynman diagrams in two-component DM model
3.2 Model

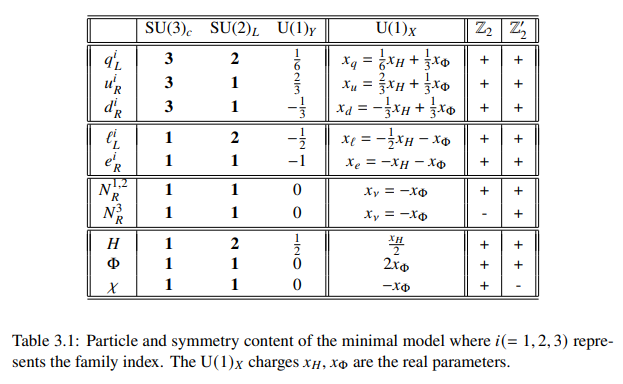
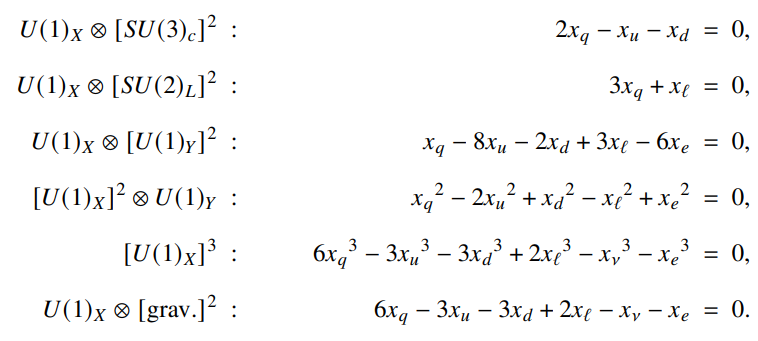
In the next subsections, we discuss various parts of the lagrangian of the model,
3.2.1 Scalar Sector


where 𝛼 is the mixing angle. The rotation matrix satisfies
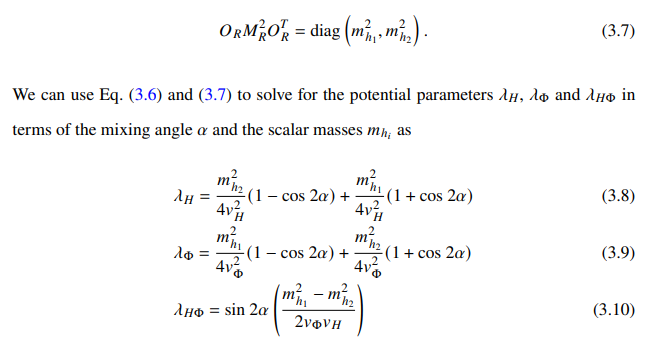
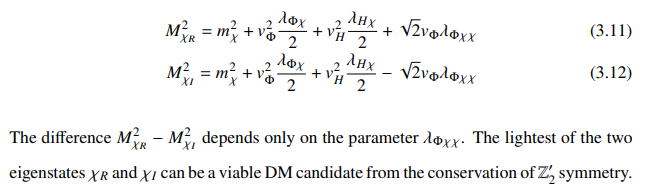
The real and imaginary components of 𝜒 have the following masses
3.2.2 Gauge sector
To determine the gauge boson spectrum, we have to expand the scalar kinetic terms and replace
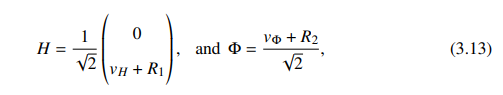

3.2.3 Yukawa sector
The Yukawa sector of the model can be written in a gauge-invariant way as

This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
Author:
(1) Shivam Gola, The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai.

